In the wake of COVID-19, mobile networks have played a pivotal role in ensuring reliable connectivity for sustaining social and economic activities in the Middle East and North Africa (MENA). As nations grapple with the pandemic’s effects, governments in the MENA region and beyond are prioritizing economic recovery and sustainable development. Digital services and mobile technologies are becoming instrumental in achieving these goals, by driving economic growth, enhancing workforce mobility, and improving industrial efficiencies.
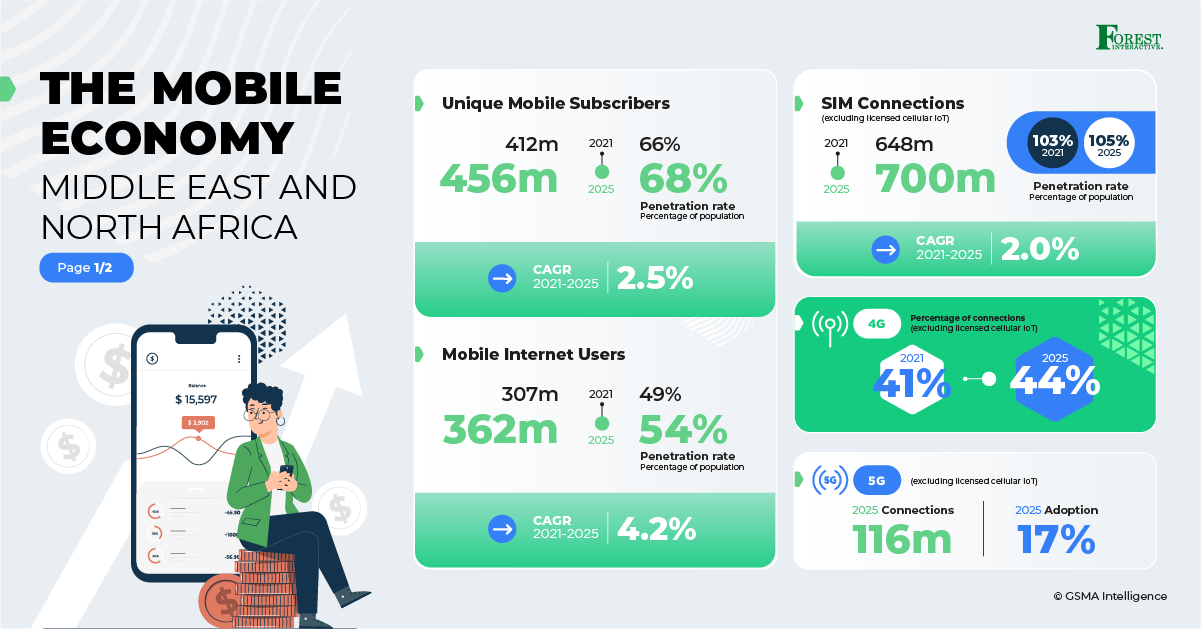
The MENA region witnessed a surge in mobile internet users, surpassing 300 million in 2021, with a projected penetration rate of 50% by the end of 2022. The Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) Arab states are leading in mobile internet usage, but challenges in connecting offline populations remain in other areas. Smartphone adoption is on the rise, particularly in less developed mobile markets, and investments in network infrastructure continue to support this growth. This expansion is expected to lead to a substantial increase in data consumption, with a 430% growth forecast between 2021 and 2027.
As of 2021, 4G technology prevails in MENA, boasting nearly 270 million connections. However, 4G adoption is expected to peak in 2023 as consumers increasingly transition to 5G plans. While 5G adoption is still in its early stages in the region, the GCC Arab states are pioneering 5G networks, aiming for 41 million 5G connections by 2025. The transition to 5G opens significant opportunities in the Business-to-Business (B2B) sector, with various digital transformation projects underway across industries. To fully seize these opportunities, MENA’s 5G leaders are focusing on new capabilities, with an emphasis on edge computing to diversify their revenue streams beyond traditional telecom services.
Additionally, sustainability and security are paramount in the network transformation strategies of MENA operators. With the increasing focus on energy efficiency and the utilization of cloud and IT technologies, the region is aligning itself with global technology trends. Open networking technologies, particularly in markets with low Average Revenue Per User (ARPU), are gaining momentum as they offer cost savings and enhance flexibility in network deployment.
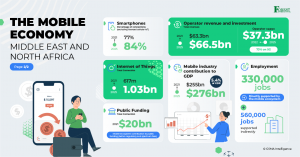
The mobile ecosystem is not only driving economic growth but also creating jobs and contributing significantly to the public sector through taxation. Mobile operators play a pivotal role in achieving the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), facilitating the growth of small businesses, digital transformation, and access to life-enhancing services and tools, such as mobile money adoption. Furthermore, operators are increasingly embracing SDG 13: Climate Action through environmental protection efforts and renewable energy-powered base stations.
In a post-pandemic world, digital connectivity is set to become even more essential for individuals, businesses, and institutions. Regulatory frameworks that foster investment will be crucial for deploying essential telecom infrastructure, which is vital for economic recovery and future crisis resilience. Realizing the full potential of the mobile opportunity will necessitate forward-looking spectrum policies, fair pricing, and technology-neutral licensing to support the growth of 5G throughout this decade and beyond. Additionally, addressing barriers to mobile internet adoption is crucial, and data protection regimes must ensure privacy, safety, and security for participants in the digital economy.
 Company Profile
Company Profile Brand Identity Guidelines
Brand Identity Guidelines