In the last few years, we have seen society’s embrace of new technology accelerate dramatically. Automation, AI, AR/VR experiences, autonomous vehicles, and robotics are innovations that push the boundaries of human progress. Today, the future of the economy and our communities depends on wireless technology that completely transforms the way telecom networks operate – 5G Non-Standalone (NSA) and 5G Standalone.
Expected to launch worldwide, mobile operators provide catalysts for innovation, new markets, and economic growth through 5G networks. However, most deployments are Non-Standalone, utilizing existing 4G infrastructure, offering enhanced Mobile Broadband (eMBB) with higher data-bandwidth, faster speeds, and lower latency.
However, industry digitalization demands more than 5G NSA permits. Therefore, mobile operators are considering investments into 5G Standalone. This move aims to unlock new network capabilities and support connectivity for vast applications like smart cities and smart manufacturing.
The connections enabled by advancing to Standalone 5G architecture will empower a vast array of new and enhanced critical infrastructure services. Let’s cover the differences between the two tracks in more detail and explain why Standalone is necessary for our future.
Building 5G Networks for Speed and Resilience

In simple terms, 5G Non-Standalone is an extension of the 4G environment with legacy technology powering cellular networks. This provides moderately faster speeds. For service providers, the NSA mode allows leveraging existing network assets. This is instead of deploying a completely new end-to-end 5G network.
NSA 5G deployments allow operators to increase mobile broadband capacity for consumers, supporting services such as fixed wireless access, high-definition video streaming, and basic cloud gaming. This is essentially an enhanced version of existing mobile technology.
However, difficult times have forced our perception of 5G to change. It’s not enough for consumer apps and services focused on entertainment, remote work, and learning to benefit from current 5G networks. Looking beyond these applications towards the many other devices or machines that 5G should enable, new networks are needed that can work independently of 4G infrastructure. Hence, the development of Standalone.
We have to achieve higher levels of performance and reliability, and Standalone can unlock the full benefits of 5G.A growing number of mobile operators want to leverage 5G Standalone. This is to secure long-term ROI and service monetization. They aim to offer new, differentiated applications to enterprise users. As a result, exploring opportunities for 5G usage in entire industries has become necessary.
Looking Beyond 5G Non Standalone to Grow Enterprise Revenue
One vital element of making 5G networks integral to future business success is supporting the entire digital ecosystem. Whether Non-Standalone or Standalone, it ultimately depends on the specific business goals of mobile operators and client requirements.
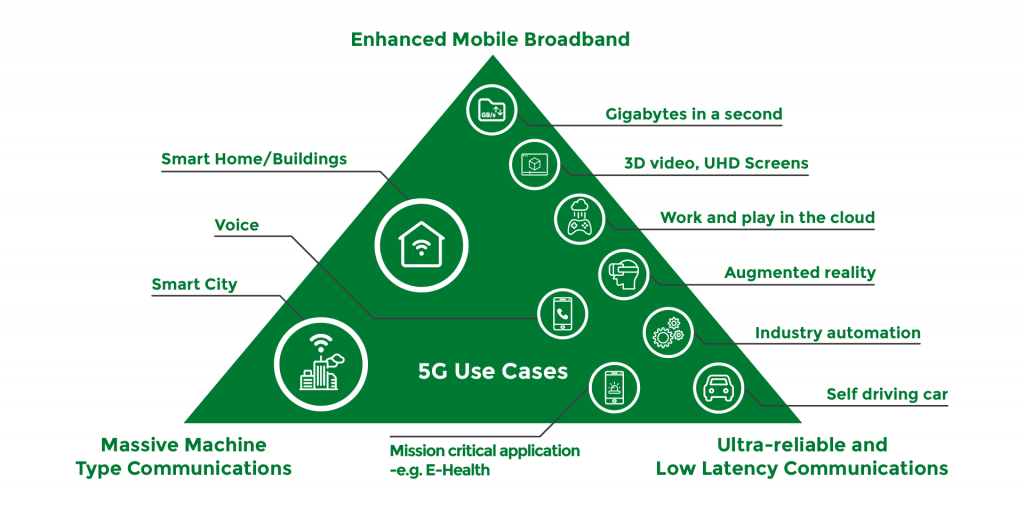
These are the 4 primary features that 5G supports that are supposed to give rise to an exciting number of new use cases.
- network slicing – enable the creation of multiple virtual networks atop a shared physical infrastructure.
- enhanced Mobile Broadband (eMBB) – high capacity, faster throughput, higher user mobility that is geared towards handsets and the replacement of landlines.
- Ultra-Reliable Low Latency Communications (URLLC) – deliver advanced services for latency-sensitive connected devices such as factory automation and autonomous driving
- massive Machine Type Communication (mMTC) – provide connectivity to many devices which transmit sporadically a low amount of traffic over billions of devices without overloading the network.
Envisioned as fully virtualized and capable of automatically provisioning custom data streams for specific applications. Standalone 5G architecture is intended for greater data capacity, localized computing, and bespoke services. As the number of connected devices increases exponentially around the world. Backhauling data from gigabit-consuming machines necessitates adopting a new cloud-native core in network infrastructure. This adaptation is crucial.
An important distinction associated with this shift to not just Standalone 5G but fully virtualized networks is that telecom networks will become more like IT networks, through software-defined networking. Specifically, Standalone enables advanced features like network slicing and elements such as the Network Exposure Function (NEF) to realize a service-based architecture.
It is plan for all 5G core functions to fully leverage a service-based architecture. This open framework will use APIs to access third-party applications, enabling faster introduction of services. At this stage, there would be even more opportunities to expand into new business models for operators.
Creating New 5G-Enabled Services
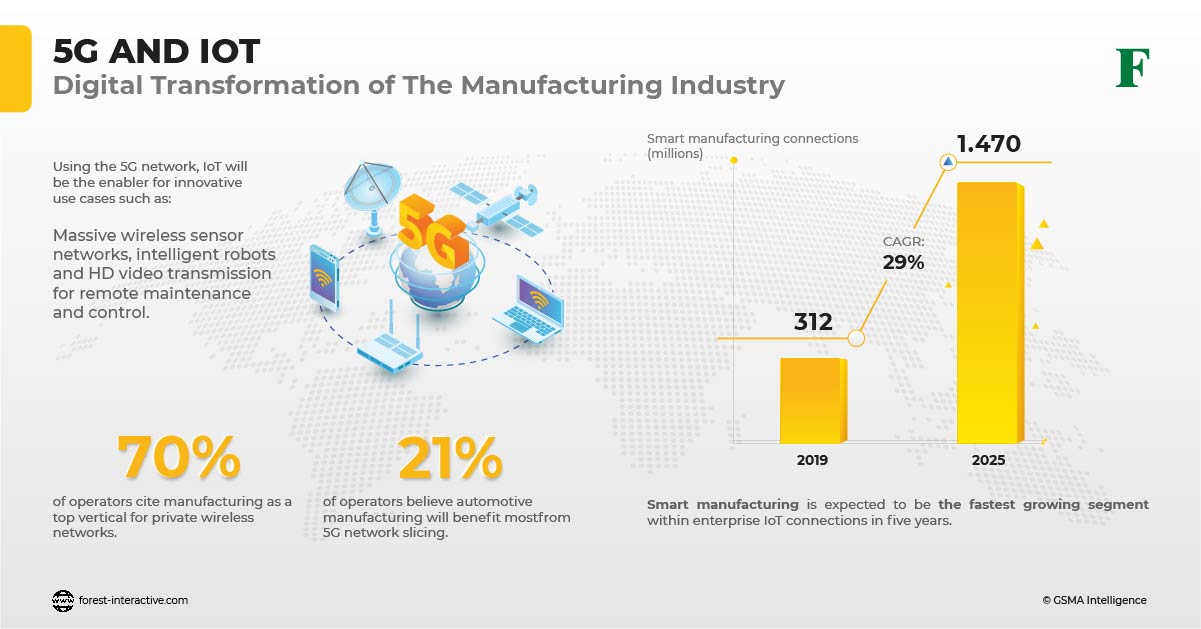
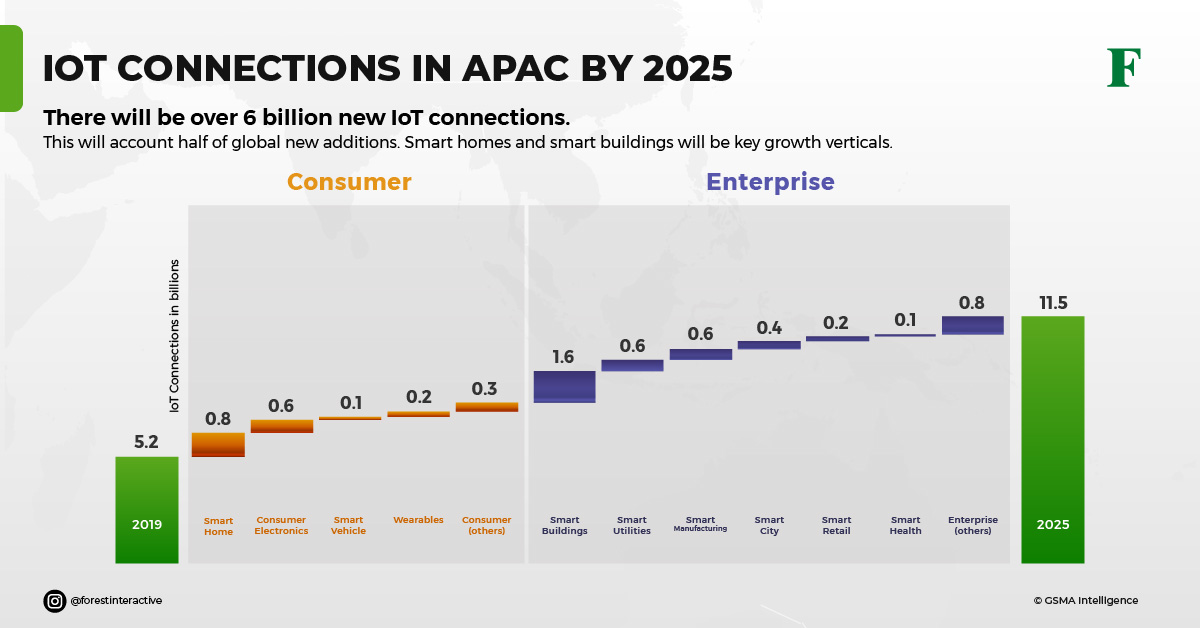
In the design and deployment of 5G networks, automatic allocation of connectivity is paramount to 5G monetization. Network slices will see the greatest usage in industrial and enterprise IoT-type implementation. This is because they can be designed, configured, and connected end-to-end according to the client’s specified requirements.
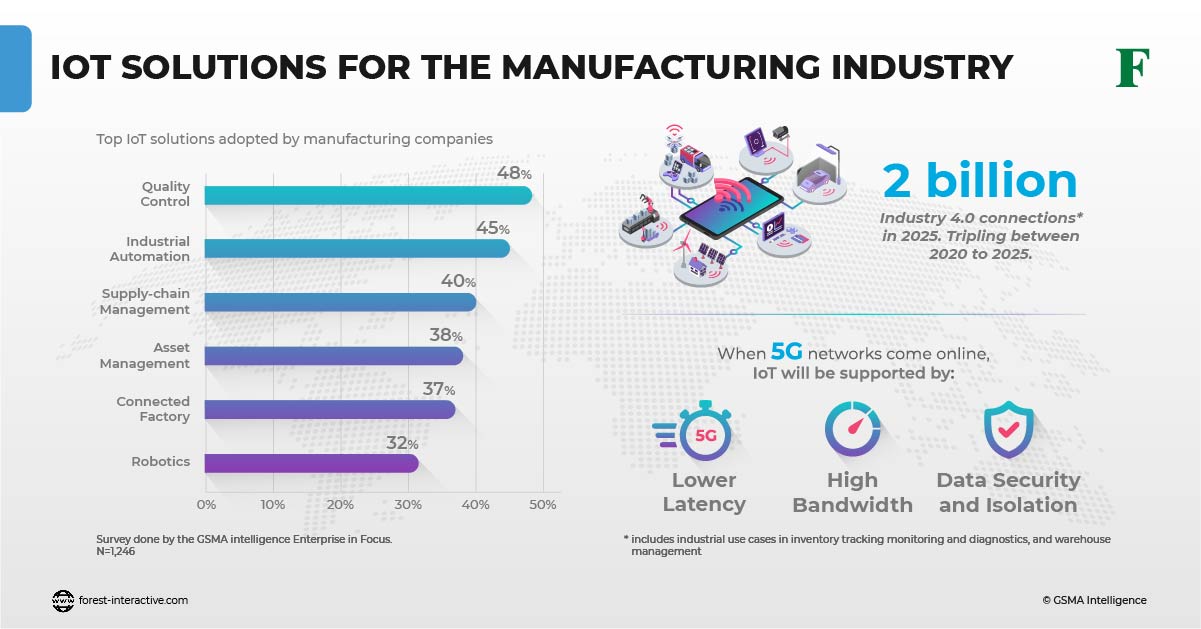
We can expect many use cases from both 5G Non-Standalone and Standalone telecom networks. However, industry verticals offer 5G the greatest opportunities to excel. It is the functionality enabled by Standalone that will provide the platform for 5G’s full benefits to emerge. Just take a look at this graph:
As long as investments and innovative thinking continue, this launch of true 5G will come sooner than we think. Necessary changes have to be made to keep up with the struggles and concerns of the time. We are dependent on modern connectivity for our daily livelihoods and at this time the single most important technology to maintain that is next-gen 5G wireless communications technology.